Ever since its medical introduction in the 1980s, elbow arthroscopy has been an accepted treatment option for a variety of elbow disorders. With advancements in technique and instruments, the treatment option has improved over the years and now accounts for more than 10% of all elbow surgeries performed in the United States each year. Considered safe and highly effective, elbow arthroscopy is easier than other types of elbow surgeries and offers faster recovery.
What is elbow arthroscopy?
Elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to inspect an elbow joint from inside and repair damages. Arthroscopy is a derivative of two Greek words conveying the meaning “to look within the joint.”
Elbow arthroscopy involves use of a micro camera inserted through a small incision to view inside the elbow joint and guide minuscule surgical instruments to repair damages.
What is the need of elbow arthroscopy?
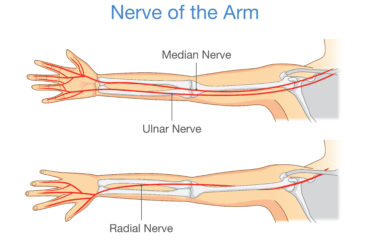
Elbow joint is the meeting place of three bones, namely humerus, radius, and ulna. The complex hinge joint has three sub joints, where these bones meet each other. A number of soft tissues, tendons, ligaments, muscles, bursae, and cartilage are there to provide strength and functional ability to the elbow. Nerves and blood vessels also pass through it providing sensation.
Any injury to the elbow is likely to damage these structures that adversely affect the joint stability. As the elbow joint is very important for the functionality of the hand, damages must be treated at the earliest and with the shortest possible downtime.
Elbow arthroscopy is used both for diagnosis and treatment purposes. It is less painful and minimally invasive and requires very small incisions to treat elbow disorders. Patients recover and return to daily activities in the shortest time compared to other surgical elbow treatments.
What are conditions treated with elbow arthroscopy?
Elbow arthroscopy is an established surgical method to treat conditions affecting your elbow, such as
- Elbow pain nonresponsive to nonsurgical methods and requiring invasive surgical intervention
- Chronic inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the elbow following an injury
- To remove scar tissues or bone and cartilage fragments restricting the joint movement
- Tennis elbow
- Arthritis of the elbow
- Osteochondritis dissecans or appearance of cracks on small bones in the elbow due to inadequate blood supply
- Debridement abnormal bony outgrowth
- Capsular releases to treat elbow stiffness
- Osteochondritis of the elbow
- Removal of bone spurs
Who is a candidate for elbow arthroscopy?
Anyone with the above mentioned disorders is fit to undergo elbow arthroscopy. There is no age bar or physical restrictions preventing patients from having the surgery.
What are elbow disorders that elbow arthroscopy not apt to treat?
Elbow arthroscopy is not an option to treat multiple fractures, golfer’s elbow, elbow joint replacements, and other disorders that require open surgical technique. The usability of the procedure is also limited in many cases due to surgeon’s knowledge of elbow anatomy and expertise in performing arthroscopy on the elbow joint.
How is elbow arthroscopy performed?
Surgeons use general anesthesia to perform elbow arthroscopy. Intravenous antibiotics may also be administered to prevent post-surgical infection. Patients are required to sleep in either of two positions – prone or side lying. A tourniquet put on the upper arm of the elbow to be operated. The arm is placed in a holder to ensure it remains in an undisturbed position.
The skin above the elbow joint is cleaned to perform the arthroscopy. Lines are drawn to mark the position of nerves, blood vessels, and bones. The elbow joint is filled with fluid to ensure clear visibility of structures inside. An arthroscope, a micro camera, is inserted into the joint through a small incision above the elbow joint. Images generated by the camera and viewed on a video screen allow surgeons to identify any problem.
Miniature, specialized surgical instruments are introduced to the elbow joint through multiple tiny incisions and the repair is performed. The skin above the joint is stitched and covered with tape after the elbow arthroscopy is completed.
How long does elbow arthroscopy surgery take?
An elbow arthroscopy takes about 60 to 90 minutes depending on the treatment required.
Do I need to stay at the hospital after elbow arthroscopy?
It is an outpatient surgery. As the procedure is minimally invasive, patients are discharged same day after a brief observation.
Is there any restriction on movement after elbow arthroscopy?
Patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 hours after surgery. The additional dressing applied on the elbow restricts the elbow movement partially. You may not be able to drive for a few days.
What are benefits of elbow arthroscopy over open surgery?
- Minimally invasive
- Smaller incisions
- Fast recovery
- Less downtime
- Minimal trauma and no scarring
- Less pain and quick healing
- Low chance of infection
- Better preservation of elbow motion
- Less chance of triggering any medical condition
How long is the recovery time after having surgery?
Elbow arthroscopy is known for quick recovery it offers. However, the recovery period varies from one week to a few months depending on patient condition and extent of surgical treatment. As it is minimally invasive, pain, swelling, and post-surgical complications are minimum. This provides a boost to early recovery. Physical therapy, adequate nutrition, and post-operative care are important factors that speed up the recuperation.
What type of post-operative rehab is required after elbow arthroscopy?
Restrictions on elbow movement remain there for 1 or 2 weeks. Patients are advised to use ice therapy and keep the elbow joint elevated during the first 2 days. They should make mild finger and wrist movements or do gentle exercises to stimulate blood circulation.
A structured exercise regimen, including physical therapy, is important to regain functional strength without any fear of reinjury.
What are post-surgical precautions patients should follow after elbow arthroscopy?
- Keep incisions dry and clean
- Take adequate rest as advised by your surgeon
- Keep the elbow raised on pillows to minimize swelling
- Use a compressive stocking to cover the entire hand after the dressing is removed
- Eat healthy
- Avoid smoking
- No forced elbow, arm, and wrist use
- No extreme elbow or hand position for 4 weeks
- Avoid overhead arm movement for 2 weeks
- No lightweight lifting for 4 weeks
What are the potential complications of elbow arthroscopy?
Elbow arthroscopy is safe and complications are rare. When performed by inexperienced surgeons, there may be risks of nerve injury, elbow stiffness, bleeding, and damage to structures within the joint.
References
Lyons TR, Field LD, Savoie FH. Basics of elbow arthroscopy. Instr Course Lect. 2000;49:239-46.
Bennett J. Michael. Elbow Arthroscopy: The Basics. Journal of Hand Surgery , Volume 38 , Issue 1 , 164 – 167.
Dodson CC, Nho SJ, Williams RJ, Altchek DW. Elbow arthroscopy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008 Oct;16(10):574-85.
Adams JE, King GJ, Steinmann SP, Cohen MS. Elbow arthroscopy: indications, techniques, outcomes, and complications. Instr Course Lect. 2015;64:215-24.
Kinaci A., Neuhaus V, Ring D. (2015). Surgical Procedures of the Elbow: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Observational Study in the United States. Archives of Bone and Joint Surgery, 3(1), 13–18.
Cefo I, Eygendaal D. Arthroscopic arthrolysis for posttraumatic elbow stiffness. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20:434–439