When someone has significant osteoarthritis of the knee, the Phoenix orthopedic surgeon will try several conservative measures before considering a knee replacement surgery. Find out about the top 8 treatments you should consider before having surgery on your knee.
1. Exercise and Weight Loss
One of the most important aspects of nonsurgical management of knee arthritis is weight loss and strengthening. For every pound of weight, there is six pounds of pressure on the knee j oint with activity. Overweight people also tend to develop arthritis at an earlier age than slimmer individuals.
oint with activity. Overweight people also tend to develop arthritis at an earlier age than slimmer individuals.
Muscle strength is crucial when fighting knee osteoarthritis. The knee joint muscles act as shock absorbers for the pressures of sporting activities, as well as regular life activity. Strong muscles support the knee joint and prevent stress. This decreases the symptoms of arthritis. Exercises that increase hamstring, quadricep, and calf strength include leg presses, leg extensions, and squats. These exercises should not produce pain. Also, any cardiovascular exercise will be beneficial for weight loss, such as elliptical, cycling, swimming, and rollerblading.
2. Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications are often used for knee arthritis to decrease symptoms. These are available by over-the-counter means or prescription. Examples of OTC NSAIDS include ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen (Aleve), and aspirin. Prescription NSAIDS include Celebrex, Mobic, Daypro, and Relafen. Also, acetaminophen (Tylenol) is often used for knee arthritis pain.
3. Bracing
For the treatment of medical compartmental osteoarthritis of the knee joint, knee braces offer some relief of pain and stiffness. The brace works by unloading the inside aspect of the knee, and it can be custom-made or factory shipped.
4. Nutritional Supplements
The most commonly recommended nutritional supplements for knee arthritis are glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. While these are commonly used, they are not regulated by the FDA. Glucosamine is an aminomonosaccharide, and is the primary component of connective tissue and cartilage. Chondroitin sulfate is found in proteoglycans, and it contributes to cartilage stability. When uses as a supplement, chondroitin is derived from bovine cartilage. Several research studies are currently being conducted to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and usefulness of these nutritional supplements for knee arthritis.
5. Viscosupplementation
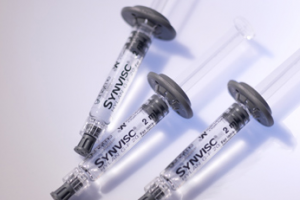 The knee joint contains synovial fluid that is highly viscous. This fluid gives the knee a friction-free environment and contains hyaluronic acid. For healthy adults, synovial fluid hyaluronic acid has a molecular weight of around 4 – 5 million. This acid binds to proteoglycans to stabilize the articular cartilage and give the joint elasticity and viscosity. For someone with arthritis of the knee, the molecular weight of the hyaluronic acid decreases, causing problems with increased friction, loss of mobility, and abnormal joint movement.
The knee joint contains synovial fluid that is highly viscous. This fluid gives the knee a friction-free environment and contains hyaluronic acid. For healthy adults, synovial fluid hyaluronic acid has a molecular weight of around 4 – 5 million. This acid binds to proteoglycans to stabilize the articular cartilage and give the joint elasticity and viscosity. For someone with arthritis of the knee, the molecular weight of the hyaluronic acid decreases, causing problems with increased friction, loss of mobility, and abnormal joint movement.
Viscosupplementation is a form of lubrication to provide the joint with a substance that allows for shock absorption, decreases friction, and slows the osteoarthritis progression. Hylagan injections are given into the knee once a week for a series of three shots, and this series can be repeated in six months.
6. Cortisone Injections
It has been common practice for years for Scottsdale orthopedic surgeons to use cortisone injections to treat knee arthritis. This medication injected into the knee joint acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. However, research shows that the articular cartilage deteriorates after repeated cortisone injections, so caution must be used when considering this form of treatment.
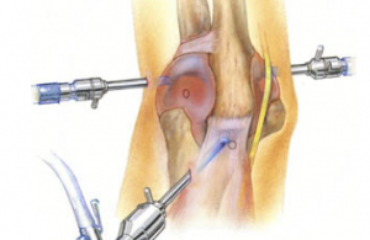
7. Abrasion/Microfracture
Abrasion arthroplasty, which is also called microfracture, is a procedure used by Phoenix knee doctors to treat knee arthritis that involves small areas of exposed bone or complete loss of cartilage. When the bone is treated, the surgeon uses a device to stimulate the bone to grow scar cartilage over the previously exposed, thinned region. This results in cartilage regrowth, which assists with mobility.
8. Chondroplasty
Another nonsurgical treatment for knee arthritis is chondroplasty. This is a smoothing of the rough articular cartilage to decrease joint friction. The surgeon uses an arthroscope to view the diseased region, and chondroplasty prevents further thinning of the cartilage surface.