The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main knee structures. An ACL injury is any over-stretching or tearing of this ligament. ACL tears can be partial or complete. Most ACL tears occur in the midsection of the ligament, or result in the ligament being completely torn from the thigh bone.
How common are anterior cruciate ligament injuries?
In the U.S. population, the overall incidence of ACL injuries is not known. However, in a New Zealand study, the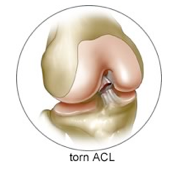 incidence was reported at 37 injuries per 100,000 person-years. According to statistics, there are around 90,000 ACL repairs performed each year in America. ACL injuries are more common in young athletes.
incidence was reported at 37 injuries per 100,000 person-years. According to statistics, there are around 90,000 ACL repairs performed each year in America. ACL injuries are more common in young athletes.
What is the purpose of the ACL?
There are four main ligaments connecting the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). These include:
- MCL – The medial collateral ligament (MCL) runs on the inside of the knee, and it prevents the knee from bending inward.
- LCL – The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) runs along the outer portion of the knee, and it prevents the knee from bowing outward.
- PCL – The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) works with the ACL, and it prevents the shin bone from sliding under the femur.
- ACL – The ACL is in the middle area of the knee, and it prevents the shin bone from going in front of the thigh bone.
What causes an ACL injury?
ACL injuries may occur along with other structural injuries. An ACL tear commonly occurs with a MCL tear, as well as with a tear of the lateral meniscus (shock-absorbing cartilage). An ACL injury may occur if you:
- Overextend the knee joint
- Get hit hard on the side of the knee (football tackle)
- Quickly stop moving and change direction during running, turning, or landing
What sporting activities are associated with ACL injuries?
Football, soccer, and basketball are sports associated with ACL tears and injuries.
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
Early symptoms include a popping sound heard at the time of the injury, knee swelling within six hours of the initial trauma, pain that is worse with weight-bearing, and a feeling of knee instability (gives way).
How are ACL injuries diagnosed?
The Phoenix orthopedic surgeon will inquire about your symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. The MRI is used to assess the extent of the injury and to confirm the diagnosis.
How are anterior cruciate ligament injuries treated?
If your trainer suspects an ACL injury, he will have you:
- Elevate the leg above heart level.
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen.
- Use ice packs for 20-minute intervals.
- Use crutches until you see the doctor.
Will I need surgery?
Surgery is used to repair partial and complete tears of the ACL. Unrepaired ACL tears can lead to further knee joint damage. The surgery is performed by a Phoenix sports medicine doctor using arthroscopic technique (use of a tiny camera and small instruments). Several small incisions are made around the knee, and the Scottsdale orthopedic surgeon inserts the camera and instruments through these incisions to make necessary repairs. Following surgery, you will need physical therapy to improve leg strength and joint range of motion.
The top orthopedic doctor in Phoenix for ACL injuries is Dr. Adam Farber with Phoenix Shoulder and Knee. The outcomes with ACL procedures have been nothing short of phenomenal! Call (480) 219-3342 today!
Resource
Gianotti SM, Marshall SW, Hume PA, Bunt L. Incidence of anterior cruciate ligament injury and other knee ligament injuries: a national population-based study. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(6):622–627.
McCarroll JR, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in the young athlete with open physes. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(1):44–47.