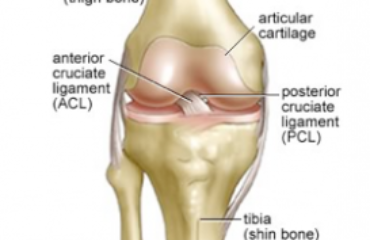
Joint pain is referred as aches, discomfort, and soreness of any body joint. The knee joint is affected by chronic pain more than any other joint in the body. The main cause of chronic knee pain is arthritis, which also is associated with swelling, tenderness around the joint, and loss of function.
Causes of Knee Pain
The treatment of chronic knee pain depends on the cause. Common causes of knee pain include:
- Arthritis – This condition leads to joint cartilage wear-and-tear, which then causes a painful sensation due to bones
 gliding over each other.
gliding over each other.
- Patellar tendonitis – This is caused by inflammation or irritation of one or more knee tendons (thick, fibrous tissues that attach muscles to bones).
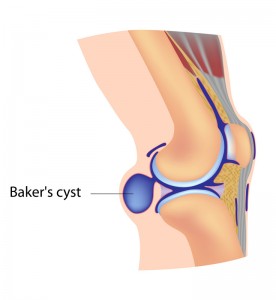
- Baker’s cyst – A fluid-filled cyst that causes a lump at the posterior area of the knee. The cyst leads to difficulties with movement and tightness.
- Bursitis – Knee injuries cause inflammation in the small sacs of fluid in the knee (bursae).
- Injuries – This may cause small fragments of cartilage or bone to break off and get stuck in the joint.
- Tendinitis – This condition causes swelling of the joint tendons (jumper’s knee).
Treatment Options
There are several options for knee pain. Treatment includes:
- Rest – Taking a break from your normal/usual activities and workouts will relieve joint pain.
- Ice and heat application – Inflammation and pain respond well to ice therapy, and warm compresses can soothe tight muscles.
- Compression – Using an ACE wrap (compression bandage) prevents swelling and supports normal knee alignment.
- Physical therapy – The therapist works with you to strengthen the muscles around the knee to make them stable. In addition, therapy is used to prevent injuries or worsening of an injury. The therapist uses electrical stimulation, ultrasound therapy, and cold packs to alleviate knee pain.
- Arthroscopic knee surgery – This procedure involves making small incisions around the knee and using a fiber optic camera scope to view the joint. The doctor examines the knee for loose pieces of bone or cartilage, which is
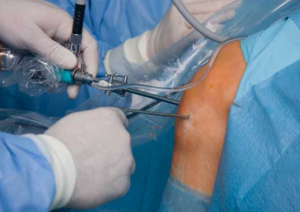 removed using special tools.
removed using special tools.
- Knee replacement – For severely damaged knee joints, a total knee replacement is done. This involves removal of worn bone ends and replacing these with metal and/or plastic components (called prostheses).
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy – To stimulate knee joint tissue growth and repair, the doctor can inject a PRP solution. Blood is drawn from the patient, and the platelets are separated via centrifuge in the laboratory. The PRP solution is then injected into the knee joint.
- Corticosteroid injections – The knee joint can be injected with a corticosteroid agent. The steroidal agent will decrease inflammation and relieve joint pain. This procedure is safely done in the doctor’s office.
- Hyaluronic acid injection – The knee can be injected using hyaluronic acid solution. This substance mimics joint synovial fluid, lubricates the joint, and eases bone friction pain.
- Medications – Depending on the severity of your knee pain, medications are used. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, will alleviate joint pain associated with inflammation. Chronic knee pain can also be treated using Ultram, Lorcet, or Darvocet.
- Losing weight – Maintaining a healthy weight is the best thing you can do for your knees. Because added or extra weight puts a strain on your joints, decrease your risk of arthritis and injuries by losing weight.
- Staying in shape – Exercise is a good way to strengthen the muscles that support your knee joints. Not only will exercise relieve knee pain, it will help your overall health status.
Dr. Adam Farber at Phoenix Shoulder and Knee is a top knee specialist in Arizona. He offers comprehensive treatment options for chronic knee pain including medications, injections and surgery when necessary. As a fellowship trained surgeon, he is an expert in all minimally invasive treatment options available.
Call us today!